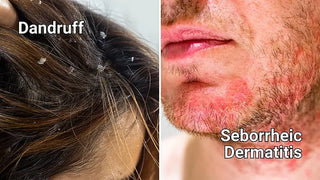
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common, chronic skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It’s characterized by red, scaly patches and stubborn dandruff, and can cause significant discomfort and impact self-esteem.
Gaining a thorough understanding of seborrheic dermatitis is essential for effectively managing it and finding suitable seborrheic dermatitis treatments. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, with a particular focus on seborrheic dermatitis treatment for the face and scalp.
What is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that primarily affects areas with a high concentration of oil-producing (sebaceous) glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper body. It causes red, scaly patches, itching, and dandruff, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe.
While seborrheic dermatitis shares some similarities with regular dandruff, such as flaking and itching, unlike dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis also involves inflammation of the skin and often affects areas beyond the scalp. The patches associated with seborrheic dermatitis are typically oilier, more persistent, and more prone to redness and irritation than regular dandruff.

The most commonly affected areas in seborrheic dermatitis include the scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, sides of the nose, backs of the ears, and the chest. In some cases, it can also appear on other oil-rich areas of the body, such as the armpits and groin.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a complex condition with several contributing factors. In this section, we will explore the various causes of and risk factors associated with seborrheic dermatitis.
Malassezia Yeast
Malassezia species, lipophilic yeasts found on human skin, are believed to play a role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis, particularly in lipid-rich areas like the face, scalp, and trunk. While the exact mechanism remains unclear, the proliferation of these yeasts is thought to trigger an immunological response, leading to inflammation and seborrheic dermatitis flares. Malassezia species also produce toxic metabolites, lipases, and reactive oxygen species that can irritate the skin and cause a seborrheic dermatitis flare-up in predisposed individuals. Strong evidence of the involvement of Malassezia in seborrheic dermatitis comes from the reduction in yeast numbers, and the subsequent improvement of seborrheic dermatitis symptoms, after treatment with antifungals. This suggests that the yeast and its metabolites play a crucial role in the condition's development and pathogenesis.
Genetic Predisposition
There is evidence to suggest that genetic factors may also play a role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis.
While the role of genetics in the development of seborrheic dermatitis is not yet fully understood, it is believed that a family history of seborrheic dermatitis or related skin conditions, such as atopic dermatitis, may increase an individual's susceptibility. Genetic predispositions could potentially influence immune responses to the Malassezia yeast, leading to a more profound inflammatory response. Genetic factors may also affect skin surface lipids, influencing the colonization and growth of Malassezia on the skin.
Hormonal Factors
Hormones, particularly androgens, play a crucial role in the development of seborrheic dermatitis by influencing sebum production. The increased sebum during puberty provides a nourishing environment for Malassezia species. These yeasts break down lipids, triggering inflammation and the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Hormonal imbalances, such as polycystic ovary syndrome, can also heighten seborrheic dermatitis risk.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors can also contribute to the development of seborrheic dermatitis. Factors such as climate, humidity, and seasonal changes may exacerbate or trigger seborrheic dermatitis symptoms. Cold and dry weather conditions for instance, can lead to skin dryness and increased seborrheic dermatitis flares, while hot and humid climates may promote the growth of Malassezia species, further contributing to seborrheic dermatitis. Exposure to irritants, allergens, and harsh chemicals in personal care products can aggravate seborrheic dermatitis in predisposed individuals.
Weakened Immune System
While the exact mechanism between a weakened immune system and the development of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, the prevalence of seborrheic dermatitis is higher in immunocompromised individuals, particularly among patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is likely that a weakened immune system makes individuals more susceptible to developing seborrheic dermatitis due to a reduced ability to regulate the inflammatory response to Malassezia species and other triggering factors.
By understanding the various factors that contribute to seborrheic dermatitis, individuals can better manage their condition and seek appropriate treatments to alleviate their symptoms.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Symptoms and Diagnosis
Seborrheic Dermatitis Symptoms
Seborrheic dermatitis presents a variety of symptoms that can affect different areas of the body. Common symptoms include:
-
Scalp. Itching, redness, and flaking are typical symptoms on the scalp. In more severe cases, thick, greasy scales may form, and hair loss can occur due to persistent scratching and inflammation.
-
Face. Affected areas on the face, such as the eyebrows, eyelids, and the sides of the nose, can display redness, scaling, and itching. The skin may also appear oily or greasy.
-
Other body areas. Seborrheic dermatitis can also affect other oil-rich regions, such as the chest, armpits, and groin. In these areas, symptoms may include redness, itching, and scaly patches.
-
Severity. The severity of seborrheic dermatitis symptoms can range from mild to severe, with some individuals experiencing occasional flare-ups, while others may have persistent symptoms.
Diagnosing Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis can often be diagnosed based on its characteristic symptoms, such as red, scaly patches and itching in oil-rich areas of the body. While self-diagnosis is possible, it can be useful to consult a healthcare professional about your condition since several other skin conditions, like psoriasis, eczema, or fungal infections, share similar symptoms to seborrheic dermatitis and may require different treatments.
Conditions that can be confused with seborrheic dermatitis include psoriasis, atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, and fungal infections like tinea versicolor.
Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatment and Prevention, and Maintenance
Seborrheic Dermatitis Scalp Treatment
-
Medicated shampoos. Over-the-counter medicated shampoos containing active ingredients such as ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione, and salicylic acid can help alleviate scalp symptoms. These shampoos target the Malassezia yeast and reduce inflammation, itching, and flaking. Salicylic acid, as always, is our ingredient of choice since it also has anti-inflammatory properties and provides other benefits for the skin that you can learn about here. We’ve also formulated a Salicylic Acid Shampoo for individuals prone to seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp that you can find out more about here.
-
Topical corticosteroids. For more severe cases, a healthcare professional may prescribe a topical corticosteroid to reduce inflammation and itching. These should only be used under medical supervision and for a short period, as prolonged use can cause severe side effects.
-
Anti-fungal creams and lotions. In some cases, anti-fungal creams or lotions may be recommended to manage the yeast overgrowth contributing to seborrheic dermatitis symptoms.
-
Natural remedies and lifestyle changes. Having a balanced diet, managing stress, and practicing good scalp hygiene, including washing your hair everyday with a gentle, pH balanced shampoo like our Clarify & Rebalance Shampoo, can help prevent flare-ups and maintain scalp health. Regular hair-washing is essential to prevent the build up of oils, grime and hair products that can irritate the scalp and be used by the Malassezia yeast as food to proliferate.

Seborrheic Dermatitis Face Treatment
If you have seborrheic dermatitis on your face, having a simple, gentle skincare routine formulated with ingredients that could trigger the condition is essential. Bear in mind that a lot of otherwise really fantastic ingredients for your skin, including most plant oils like sunflower seed oil and grapeseed oil, can trigger seborrheic dermatitis.
If you have seborrheic dermatitis, here’s a recommended skincare routine, formulated without triggers, that you could follow in order to bring and keep the condition under control.
-
Morning. Wash your face with the AccuFix Hydrating Gentle Daily Cleanser. Moisturize, while your skin is still damp, with AccuHydra Hydrating Gel Crème or with Crème B3-B5-E with 4% niacinamide. Follow up with any one of the three variants of the AccuFix Ultimate Sunscreen.
-
Night. Wash your face with the AccuFix Hydrating Gentle Daily Cleanser. Moisturize, while your skin is still damp, with AccuHydra Hydrating Gel Crème or with Crème B3-B5-E with 4% niacinamide. If your seborrheic dermatitis is under control (not inflamed), you can also try to incorporate the AccuFix Salicylic Acid Emulsion 2-3 times per week into your skincare routine at night. Salicylic acid helps keep the growth of the Malassezia yeast in check. It also has anti-inflammatory properties and helps control excess oil production.

Other general tips include the following:
-
Ensure that the products you’re using are gentle and fragrance-free, in addition to being formulated without tiggers. Fragrance is the single most common allergen in skin care products.
-
Avoid harsh and abrasive products, including physical scrubs, and limit the use of makeup. Ensure that your makeup is also formulated without Malassezia triggers.
-
Build a skincare routine that works for you and ensure that you continue even once the condition is under control to prevent it from flaring up again.
-
As in the case of seborrheic dermatitis on the scalp, having a balanced diet and managing stress can also help prevent flare-ups of the condition elsewhere on the body.
-
Identify potential triggers and take steps to avoid them. Promptly address symptoms if and when they do arise, to help minimize the impact of seborrheic dermatitis on your daily life and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Seborrheic dermatitis is a complex skin condition that can affect various areas of the body, including the scalp, face, and other oil-rich regions. By understanding its causes, symptoms, and available treatments, you can effectively manage the condition and find relief from any associated discomfort and irritation.
A proactive and informed approach to seborrheic dermatitis care can help you minimize the impact of this condition on your daily life so you can enjoy improved skin health and comfort.
As always, you can also reach out to us for a free skin and hair care consultation on our WhatsApp number: 0302-2228349.